The subsequent queries parse all the text files using SQL, which contain names of babies born in the U.S. where the individual has a Social Security Number and segmented by state, into a single table called name_table. Names with less than 5 occurrences are omitted from this collection.
The text files are sourced from the Social Security Administration and the files can be downloaded from my GitHub directory.
The name_table contain records of names with the corresponding fields such as state, gender, year, and total number of occurrences per year within all 50 states and the District of Columbia for the year 1910-2015. In the event of a tie on the number of occurrences of names, the ranking of names are sorted alphabetically.
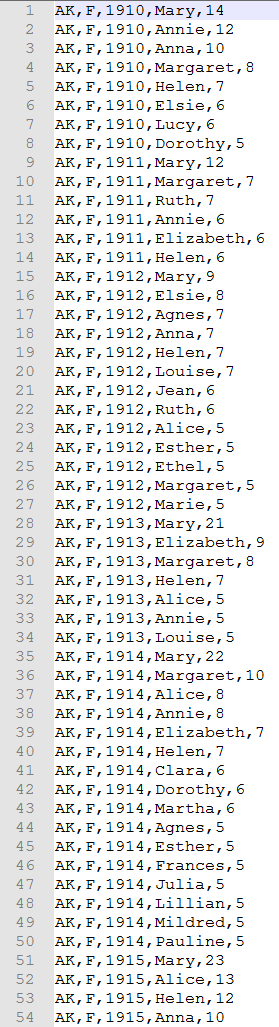
A preview of the first 54 rows out in the AK.txt file containing the names recorded from Arkansas during year 1910-2015 (27,144 rows in total):
BULK INSERT name_table FROM 'C:\Users\Michael\Downloads\namesbystate\ca.txt'
With (FIELDTERMINATOR = ',', ROWTERMINATOR = '\n');
CREATE TABLE name_table (
state_name VARCHAR(2),
gender_name VARCHAR(1),
year_name int,
name_name VARCHAR(60),
count_name int
);
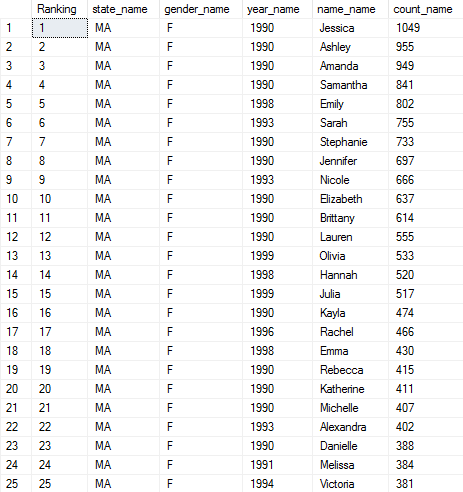
1) This common table expression (CTE) below returns the female name with the highest number of occurrences and the year at its height of popularity during 1990 to 2000 in Massachusetts:
WITH Myrowset
AS
(
SELECT
state_name, gender_name, year_name, name_name, count_name, row_number() OVER(Partition by name_name ORDER BY count_name desc) AS rownumber
FROM
name_table
WHERE
gender_name = 'f' and state_name = 'ma'
GROUP BY
state_name, gender_name, year_name, name_name, count_name
HAVING
concat(10 * floor(year_name / 10), '-', (10 * floor(year_name / 10)+ 10)) = '1990-2000'
)
SELECT dense_rank() OVER(ORDER BY count_name desc) AS Ranking, state_name, gender_name, year_name, name_name, count_name
FROM myrowset WHERE rownumber < 2 ORDER BY count_name desc, name_name asc;
Output (1527 rows):
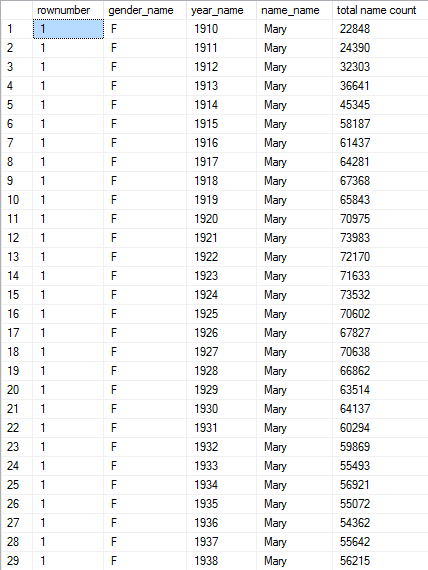
2) This CTE query determines the most popular female name from the very creation of the SSA from 1910 to 2015:
WITH Myrowset
AS
(
SELECT
row_number() OVER(Partition by year_name ORDER BY sum(count_name) desc) AS rownumber,
gender_name, year_name, name_name, sum(count_name) AS 'total name count'
FROM
name_table
WHERE
gender_name = 'f'
GROUP BY
gender_name, year_name, name_name
)
SELECT *
FROM myrowset WHERE rownumber < 2 ORDER BY year_name;
Output (106 rows):
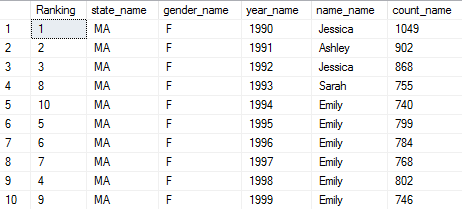
3) This CTE query returns the top female name for each year during 1990 to 1999 in Massachusetts:
WITH Myrowset
AS
(
SELECT
state_name, gender_name, year_name, name_name, count_name, row_number() OVER(Partition by year_name ORDER BY count_name desc) AS rownumber
FROM
name_table
WHERE
gender_name = 'f' and state_name = 'ma'
GROUP BY
state_name, gender_name, year_name, name_name, count_name
HAVING
concat(10 * floor(year_name / 10), '-', (10 * floor(year_name / 10)+ 10)) = '1990-2000'
)
SELECT dense_rank() OVER(ORDER BY count_name desc) AS Ranking, state_name, gender_name, year_name, name_name, count_name
FROM myrowset WHERE rownumber < 2 ORDER BY year_name;
Output (10 rows):
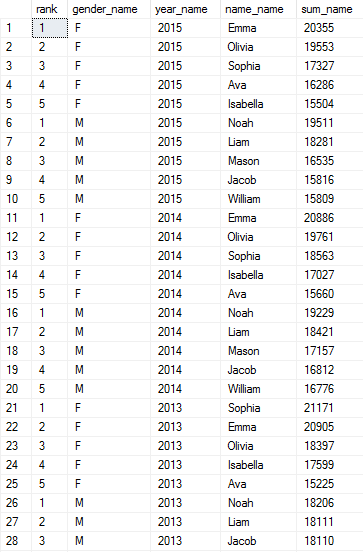
4) This CTE query returns the top five names from 1910 to 2015 by descending order:
WITH Myrowset --top 5 names for babys FROM 1910-2015
AS
(
SELECT
row_number() OVER(Partition by year_name, gender_name ORDER BY sum(count_name) desc) AS rank, gender_name, year_name, name_name,
sum(count_name) AS sum_name
FROM
name_table
GROUP BY
gender_name, year_name, name_name
)
SELECT *
FROM myrowset WHERE rank <= 5 ORDER BY year_name desc;
Output (1060 rows):
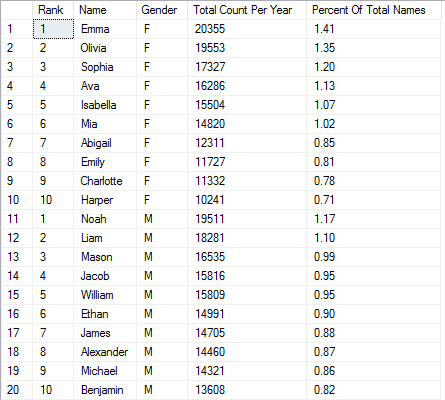
5) This CTE query finds the top ten names of both genders with accompanying percentages of all names from 2015:
WITH myrowset
AS
(
SELECT
dense_rank() over(partition by n.year_name, n.gender_name ORDER BY sum(n.count_name) desc, n.gender_name asc) AS Rank, n.name_name AS 'Name',
n.gender_name AS 'Gender', sum(n.count_name) AS 'Total Count Per Year',
cast((sum(n.count_name)* 100.0)/totalnumber AS decimal(10,2)) AS 'Percent Of Total Names'
FROM
name_table n join
( SELECT
gender_name, year_name, sum(count_name) AS totalnumber
FROM name_table
GROUP BY year_name, gender_name) AS d
ON
n.year_name = d.year_name and n.gender_name = d.gender_name
WHERE
(n.gender_name = 'm' or n.gender_name = 'f') and n.year_name = 2015
GROUP BY
totalnumber, n.name_name, n.gender_name, n.year_name
)
SELECT * FROM myrowset WHERE rank <= 10;
Output (20 rows):
6) This stored procedure returns results for regardless of gender within a specific year dependent on user input. This query is useful to look up the rank of a specific name during a year or a name beginning with a certain alphabet. Furthermore, the user can input a wildcard such as a string character ‘%’ in place of gender or name to filter a row without being limited to a specific genders or name:
CREATE PROCEDURE NameRankByYear -- stored procedure to find popular name of the year by gender
@name_input nvarchar(50),
@gender_input nvarchar(50),
@year_input int
AS
SELECT
r.rank AS 'Rank', n.name_name AS 'Name', n.gender_name AS 'Gender', sum(n.count_name) AS 'Total Count', n.year_name
FROM
name_table n join (SELECT name_name, year_name, gender_name, DENSE_RANK() over(partition by year_name, gender_name ORDER BY sum(count_name) desc) AS rank FROM name_table GROUP BY name_name, year_name, gender_name) r
ON
n.name_name = r.name_name
and n.gender_name = r.gender_name and n.year_name = r.year_name
WHERE
n.name_name LIKE Concat('%', @name_input, '%') and n.gender_name LIKE Concat('%', @gender_input, '%') and n.year_name = @year_input -- like is used to match similar names to name_input and to return all rows WITH wildcard '%' AS user input
GROUP BY
n.name_name, r.rank, n.gender_name, n.year_name
ORDER BY
r.rank, n.name_name;
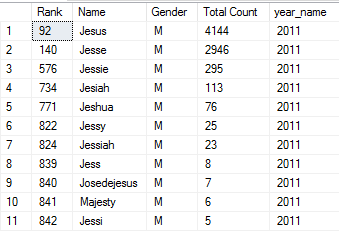
EXEC NameRankByYear @name_input = 'Jes', @gender_input = 'm', @year_input = 2011
In the query above, I am filtering rows for male names that contain the letters “jes” in the name and those who were born in 2011. I am particularly a huge fan of the name Josedejesus.
Output (11 rows):